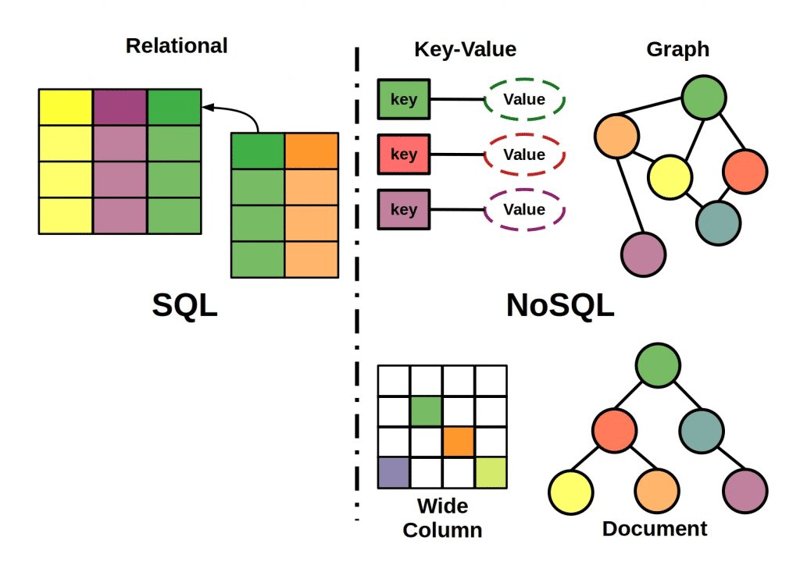
Choosing the right database technology for your system
Databases are the backbone of modern data-driven applications. Whether you’re developing an e-commerce platform, a social media app, or enterprise software, choosing the right database is critical. The two primary types of databases used today are SQL (Structured Query Language) and NOSQL (Not Only SQL) databases, with a growing number of cloud-based data stores entering the picture.
This blog will compare and contrast several popular databases, including Microsoft SQL, Oracle DB, MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, MySQL, and PostgreSQL, along with their best practice use cases. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each and how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
SQL Databases: Structured, Rigid, and Relational
SQL databases, also known as Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS), store data in tables with predefined schemas. They rely on structured data and are best suited for use cases requiring consistency, relational data, and complex queries.
1. Enterprise Databases: IBM Db2, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle DB,…
- Strengths:
- Industry-standard RDBMS, widely used in enterprises.
- Highly reliable with strong ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties.
- Advanced features like partitioning, multi-version concurrency control (MVCC), and support for large-scale transactions.
- Extensive support for enterprise features like complex business logic and optimization.
- Strong integration with other cloud products and frameworks.
- Advanced security features.
- Scalability through clustering and replication.
- Best Use Case: Mission-critical systems and large enterprise applications, especially those in finance, telecommunications, healthcare, retail, and large-scale business applications where consistency, reliability, high availability, and complex queries are essential
2. Open-source Databases: MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, …
- Strengths:
- Open-source, cost-effective, highly extensible, and supports advanced data types (e.g., JSON, HSTORE).
- Great performance for read-heavy applications.
- Options that are simple to manage and widely supported in cloud environments (e.g., AWS RDS, Google Cloud SQL).
- ACID-compliant and supports complex queries and transactions.
- Flexible deployment options from on-premise to in the cloud.
- Strong community and developer tools.
- Best Use Case: Depending on which open-source DB is used, they provide functionality that ranges from small to medium-sized businesses, web applications, and platforms that require a simple, reliable relational database without complex configurations to applications needing advanced functionality, such as geospatial queries (PostGIS), complex reporting, and real-time analytics.
3. Best Practices for SQL Databases
- Use Cases: Applications with complex relationships between data (e.g., financial systems, customer relationship management (CRM) tools, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems).
- Best Practices: Design normalized schemas, use indexes to speed up queries, leverage transactions for data consistency, and ensure database security through encryption and access control.
NOSQL Databases: Flexible, Scalable, and Schema-less
NOSQL databases are designed to handle unstructured or semi-structured data and are often optimized for scalability, high availability, and flexibility. They can be categorized into several types, including document stores, key-value stores, column-family stores, and graph databases. Below, we’ll group the most popular NOSQL databases, highlight their strengths, and identify the best use case scenarios.
1. Document Stores
Document stores organize data in flexible, schema-less formats, typically using JSON, BSON, or XML to store individual “documents.” These databases are ideal for managing unstructured or semi-structured data.
MongoDB
- Strengths:
- Schema-less, flexible document model (stores data in BSON format).
- Supports powerful querying capabilities, including full-text search and aggregation.
- Built for high scalability and performance with horizontal scaling (sharding).
- Strong ecosystem and developer tools.
- Best Use Case:
- Content management systems, real-time analytics, social media applications, and e-commerce platforms that require flexible data structures and scalability.
Couchbase
- Strengths:
- Multi-model support (key-value, document-oriented).
- High performance, low-latency, and easy to scale horizontally.
- Built-in caching layer for fast data retrieval.
- Supports complex queries, full-text search, and data indexing.
- Best Use Case:
- Mobile apps, IoT applications, and real-time data processing that require low-latency and flexible data management.
2. Key-Value Stores
Key-value stores are the simplest NOSQL databases, where data is stored as key-value pairs. These databases are optimized for extremely fast retrieval and high throughput.
Redis
- Strengths:
- In-memory data store with extremely fast read/write operations.
- Supports advanced data structures like lists, sets, sorted sets, and hashes.
- Ideal for caching and session management.
- Highly available with built-in replication and persistence options.
- Best Use Case:
- Caching, session storage, real-time messaging, leaderboards, and pub/sub applications.
Amazon DynamoDB
- Strengths:
- Fully managed, serverless NOSQL database optimized for high-availability, scalability, and low-latency access.
- Automatically scales to handle millions of requests per second.
- Integrated with AWS ecosystem (Lambda, S3, etc.).
- Supports both key-value and document data models.
- Best Use Case:
- Serverless applications, e-commerce platforms, IoT applications, and real-time analytics, especially when tight integration with AWS services is beneficial.
Riak
- Strengths:
- Distributed, highly available, and fault-tolerant.
- Supports automatic data replication and partitioning.
- Great for high availability and scalability across distributed systems.
- Best Use Case:
- Applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance, such as retail apps, social media platforms, and IoT services.
3. Column-Family Stores
Column-family stores store data in columns rather than rows (like relational databases). They are optimized for high-performance queries on large datasets, making them ideal for analytical and big data applications.
Cassandra
- Strengths:
- Highly scalable and distributed, ideal for handling massive amounts of data across many servers.
- Provides high availability with no single point of failure.
- Best for write-heavy workloads with low-latency reads.
- Supports eventual consistency and tunable consistency models.
- Best Use Case:
- Real-time analytics, sensor networks, recommendation systems, and applications requiring high write throughput and distributed data storage (e.g., large-scale IoT, social media).
HBase
- Strengths:
- Distributed, column-family NOSQL database built on top of Hadoop.
- Ideal for managing large datasets across clusters.
- Strong integration with Hadoop ecosystem for big data processing and analytics.
- Best Use Case:
- Big data analytics, real-time data processing, and applications in need of high scalability and fast read/write performance for massive datasets.
4. Graph Databases
Graph databases are optimized for managing highly interconnected data. They use graph structures with nodes, edges, and properties, making them ideal for applications that need to represent and traverse relationships.
Neo4j
- Strengths:
- High-performance graph processing with ACID transactions.
- Powerful query language (Cypher) for traversing relationships.
- Optimized for applications requiring complex relationship mapping and traversal.
- Best Use Case:
- Social networks, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and supply chain management, where relationships between data points are crucial for queries.
ArangoDB
- Strengths:
- Multi-model database supporting key-value, document, and graph data models.
- Supports complex graph queries and joins, while also allowing document and key-value access.
- Highly scalable and flexible.
- Best Use Case:
- Applications that require a combination of document and graph data management, such as enterprise applications with both structured and relationship-based data.
Other Cloud-Structured Data Stores
Cloud-based data stores provide an entirely different model, typically optimized for elasticity, cost-effectiveness, and automatic scaling. Many companies have moved to these stores due to their convenience, especially in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. Here are some examples of these popular systems:
1. Google Firestore (Firebase)
- Strengths:
- NOSQL document database with real-time synchronization.
- Fully managed, serverless, and scalable with strong integration into the Firebase ecosystem.
- Best Use Case: Mobile apps, real-time applications (e.g., messaging, notifications), and serverless environments.
2. Amazon DynamoDB
- Strengths:
- Fully managed NOSQL database that offers low-latency performance.
- Great for applications needing consistent, high throughput with automatic scaling.
- Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services (Lambda, S3, etc.).
- Best Use Case: Serverless applications, e-commerce platforms, gaming backends, and IoT applications.
3. Azure Cosmos DB
- Strengths:
- Globally distributed multi-model database service (supports document, graph, column-family, and key-value models).
- Offers multi-region writes and low-latency reads.
- Fully managed and scalable.
- Best Use Case: Global, mission-critical applications needing low-latency access to data across regions (e.g., global e-commerce platforms).
Key Differences and When to Choose Which Database
| Feature / Use Case | SQL Databases | NOSQL Databases |
| Schema | Rigid, predefined | Flexible, schema-less or dynamic |
| Data Model | Relational (tables, rows, columns) | Non-relational (document, key-value, graph) |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling (adds resources to a single server) | Horizontal scaling (adds more servers) |
| ACID Compliance | Strong (ensures data integrity) | Varies (e.g., MongoDB offers eventual consistency) |
| Best For | Structured data, complex transactions, reporting | Large-scale, unstructured data, flexible data types, high throughput |
| Examples | SQL Server, Oracle DB, MySQL, PostgreSQL | MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, DynamoDB |
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice with Glatco Inc. as Your Trusted Technology Partner
Choosing the right database solution for your application is a critical decision, and the complexity of today’s data-driven environments demands expertise in both SQL and NOSQL technologies. Whether you need the reliability and consistency of an SQL database or the flexibility and scalability of NOSQL databases, understanding each option’s strengths and limitations will help guide your decision.
However, finding the right solution and implementing it effectively requires more than just choosing the right database technology—it requires a trusted partner with the experience, knowledge, and resources to execute your vision.
This is where Glatco Inc. can make a real difference. As a trusted technology partner, Glatco Inc. specializes in providing custom database solutions, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or through hybrid approaches. Our team is experienced in working with a variety of databases, including Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle DB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Neo4J, and more. We can help design, implement, and optimize your database architecture to meet your specific business needs.
We focus on:
- Expert Database Design: Helping you structure your data model for performance, scalability, and maintainability.
- Cloud Database Solutions: Providing cloud-native database options like Google Firestore, AWS DynamoDB, and Azure Cosmos DB, ensuring optimal integration with your cloud infrastructure.
- Performance Optimization: From query optimization to proper indexing, we ensure your database runs efficiently, even at scale.
- Scalability: We implement horizontal and vertical scaling strategies to ensure your database can grow with your business.
- Security and Compliance: Ensuring your data is secure with encryption, regular audits, and meeting industry-specific compliance standards.
By partnering with Glatco Inc., you gain access to a team that is not only proficient in SQL and NOSQL databases but also has a deep understanding of your business requirements. We bring innovative, tailor-made solutions that drive efficiency, reduce risks, and enable you to achieve long-term success with your database infrastructure.
No matter how complex your database application needs are, Glatco Inc. is here to help you navigate the landscape of database technologies and build a robust, scalable solution that supports your business goals. Let us be your trusted partner in implementing the perfect database architecture for your future.
Let’s build something amazing together! Contact us to discuss your database project.