In the fast-paced world of software development, delivering a reliable, high-quality product is critical. Testing plays a pivotal role in ensuring that your software meets performance standards, is free from critical defects, and provides a seamless user experience. But if you’re a small or medium-sized business (SMB) with limited testing expertise, where do you start? Should you prioritize manual testing or invest in automation? This blog provides an introduction to testing approaches and actionable advice on how to implement a testing strategy that works for you.
Understanding Manual vs. Automated Testing
Manual Testing involves testers executing test cases manually without the help of automation tools. It’s ideal for:
- Exploratory testing
- Usability testing
- Small-scale or ad-hoc testing
Automated Testing, on the other hand, uses scripts and tools to execute test cases. It excels in:
- Repetitive tasks, like regression testing
- Performance testing
- Large-scale projects with frequent updates
Choosing between these approaches often depends on the size of your project, your budget, and your goals. While manual testing is crucial for uncovering user experience issues, automated testing can save time and effort in the long run for recurring tasks. In more advanced software development environments, both manual and automated testing is used.
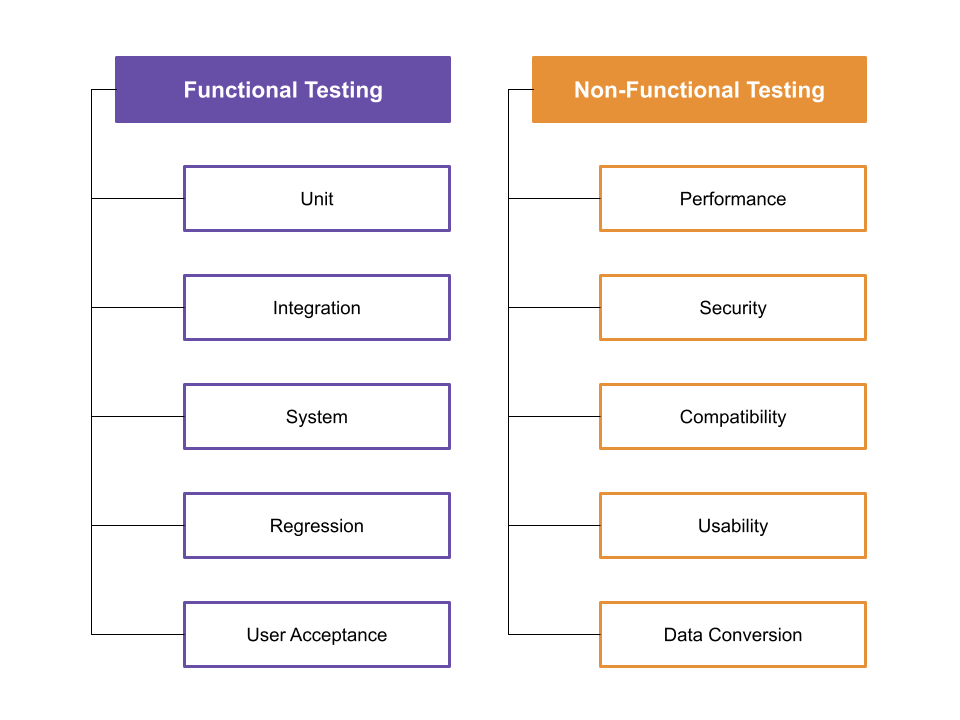
Functional vs. Non-Functional Testing
Testing can broadly be divided into two categories, and within each category, automated and/or manual testing can be performed:
- Functional Testing
- Focuses on verifying that the software performs its intended functions as per the requirements.
- Examples: Unit testing, Integration testing, System testing, and Acceptance testing.
- Non-Functional Testing
- Focuses on evaluating the software’s performance, usability, reliability, and other quality attributes.
- Examples: Performance testing, Load testing, Security testing, and Usability testing.
Both types of testing are essential to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of your software.
Types of Testing Every SMB Should Know
- Functional Testing
- Verifies that your software performs its intended functions.
- Best approach: Start with manual testing to explore basic functionality, then automate repetitive tasks over time.
- Performance Testing
- Ensures your software operates efficiently under normal and high loads.
- Best approach: Use automated tools like JMeter or LoadRunner to simulate user traffic and measure responsiveness.
- Load Testing
- Examines how your software behaves under expected user loads.
- Best approach: Automate this process with specialized load testing tools like Taurus or k6 to ensure scalability.
- Security Testing
- Identifies vulnerabilities to protect your system and user data.
- Best approach: Combine manual testing for exploratory vulnerabilities with automated tools for routine scans.
- Regression Testing
- Ensures that new changes haven’t broken existing functionality and/or impacted performance or other non-functional capabilities.
- Best approach: Automate regression tests for efficiency as your project grows.
- Usability Testing
- Evaluates your software’s user-friendliness and intuitive design.
- Best approach: Rely on manual testing with real users to gather meaningful feedback.
Steps to Kick-Start Your Testing Process
- Define Your Goals
- Identify what you want to achieve through testing (e.g., bug-free software, fast performance, secure data).
- Start with the Basics
- Begin with manual testing to understand your software’s functionality and uncover critical issues.
- Create a basic test plan and prioritize areas that need immediate attention.
- Choose the Right Tools
- For automation, explore beginner-friendly tools like Selenium, TestNG, or Postman for API testing. Many tools also offer free versions to get started.
- Adopt a Balanced Approach
- Use manual testing for creative and exploratory tasks while automating repetitive, high-volume tests to save time and resources.
- Build a Testing Culture
- Involve all team members in the testing process. Developers (unit testing), QA engineers (test plans, manual, automation, regression testing, etc.), end users (usability testing) and even non-technical stakeholders (acceptance testing) can contribute.
- Start Small, Scale Gradually
- Focus on automating a small set of repetitive tests first, such as regression testing. As your confidence grows, expand your test coverage.
What to Expect
- Early Wins: Manual testing will provide quick feedback on user experience and functionality.
- Time Investment: Setting up automation requires an initial time investment, but it will pay off with faster results in the long term.
- Learning Curve: Expect a learning curve when adopting new tools or frameworks, especially for automation.
- Improved Quality: A balanced approach to testing will improve software reliability, security, and scalability.
Final Thoughts
For SMBs, testing doesn’t need to be overwhelming or costly. Start small, focus on your priorities, and gradually adopt automation where it makes sense. By building a strong testing foundation, you’ll not only deliver better products but also gain the confidence of your users and stakeholders.
Whether you’re releasing a simple app or a complex platform, remember: testing is not just a phase; it’s an ongoing commitment to quality.
At Glatco Inc., we specialize in custom software development and understand that testing is a critical component of delivering exceptional results. With expertise in testing methodologies and tools (check out this blog). Our team ensures that your software is not only functional but also delightful to use.
Partner with Us for Top-Notch Testing
Want to ensure your software exceeds expectations? Our team is ready to help. From selecting the right QA engineers, tools to crafting comprehensive testing strategies, we’re here to take your software to the next level. Let’s build something great together—contact us today!